Topic: Electrokinetic Transport in Micro/Nano-fluidics
Speaker: Shizhi Qian
Associate Professor, Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering,
Old Dominion University, USA
Time: 14:00-16:00, (Friday) July 3, 2015
Venue: Room 249, Lee Hsun building, IMR CAS
Abstract:
Electrokinetics has emerged as one of the most promising techniques to manipulate fluid, particles and ions in micro/nano-fluidic devices, which have the potential of revolutionizing various bioanalytical applications.
The first half of this talk will be on experimental and numerical studies of electrokinetic particle transport in several types of microfluidic channels, with emphasis on dielectrophoretic (DEP) effect. The numerical predictions are in quantitative agreement with our own and other researchers’ experimental results. It has been found that the DEP effect could be utilized to separate, focus and trap particles in microfluidic devices. DEP particle-particle interactions could assemble and form particle chains parallel to the applied electric field, based on which a microfluidic device has been developed to achieve a high throughput cell electrofusion (Fig.1).
The second half of this talk will present numerical study of electrokinetic fluid and particle transport in nanofluidics. A continuum-based numerical model, which is capable of dynamically tracking the particle translocation through a nanopore with the consideration of the finite electrical double layers adjacent to charged surfaces, has been developed. The predictions on the ionic current change due to the presence of particles inside the nanopore are in qualitative agreement with existing experimental results. Furthermore, various analytical models for ionic conductance and streaming conductance in pH-regulated nanofluidics have been developed and validated by experimental data available from the literature.
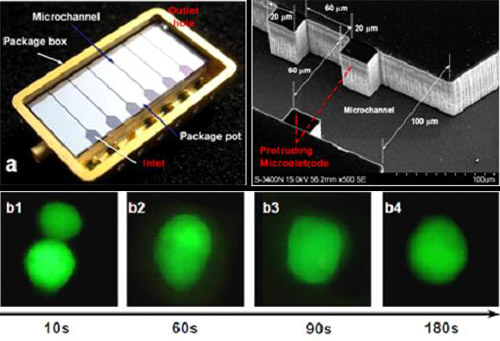
Fig.1. a high-throughput cell electrofusion microfluidic device.



